Discover the Power of LIPOTABS™ (LPT™) a patented oral liposomal tablet.
Liposomal LPT™ oral tablets (LIPOTABS™) provide a safe and more efficient way for the body to absorb nutrients, peptides and other targeted therapeutic compounds. LPT™ do not have stability problems that plague the liposomal industry – LPT™ are proven stable.
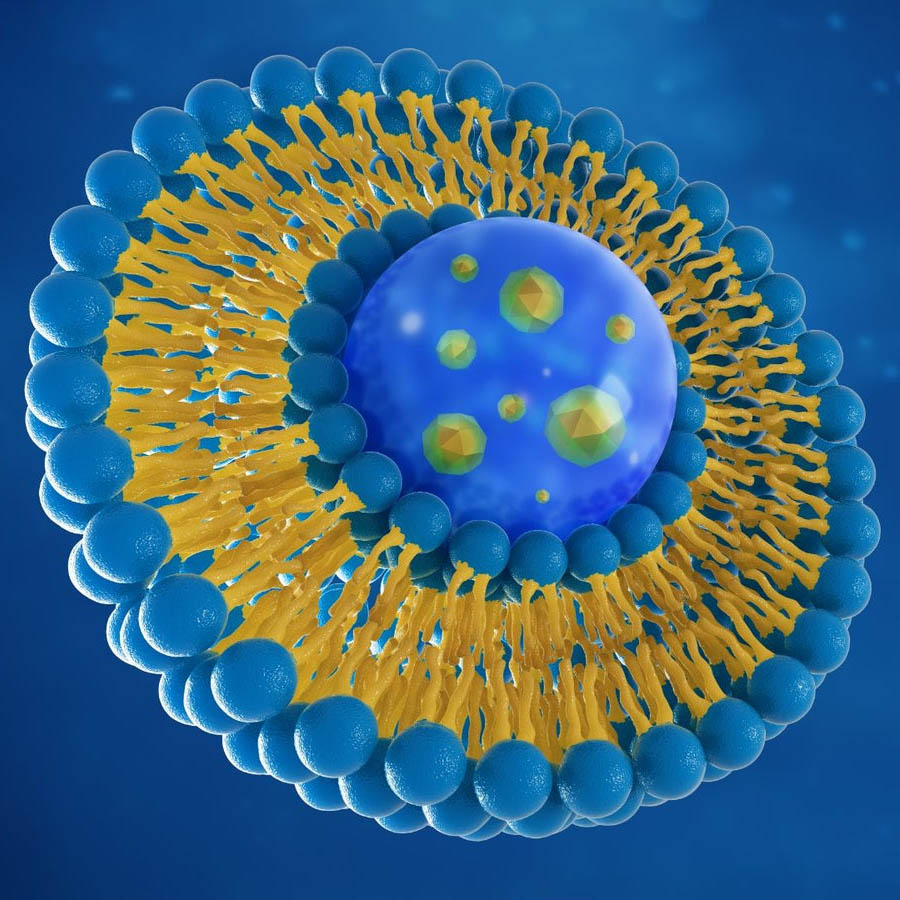
Why liposomal products?2
In general, liposomes are touted as a major advantage over regular oral delivery systems. Some of their benefits over general oral delivery include:- Greater bioavailability many drugs, oral supplements (including vitamins, minerals and other nutrients) and oral peptides have low absorption rates and poor effectiveness due to destruction in the GUT and other factors affecting GI absorption including health status, age, and foods/other supplements taken concurrently – thus the need for liposomes
- Protects therapeutic agents from GUT degradation
- Smaller doses of agents are effective
- Eliminates the need for unwanted pharmaceutical agents/additives
- Liposomes can help improve health outcomes
Liquid liposomal products on the market have
inherent stability issues including3:
- Liquid liposomes are the most popular delivery method.
- Why? They are the easiest to make.
- Liquid liposomes require heat.
- Makes product thermodynamically unstable.
- Decomposes active and inactive/inert ingredients (phospholipids).
- Liquid liposome leakage rate increases over time, which in-turn shortens the shelf-life of the product.
- Liquid liposome particles clump together to form larger and larger particle size.
- Liquid liposomes reported to grow from 100nm size to 3000nm over a 30-day period4.
- Larger particle size means less bioavailable.
- Larger size also means increased potential for side-effects.
Most liposomal product particle size on the market are 100-300nm, whereas LIPOTABS™ are 70nm in size on average, which increases their absorption and clinical effects.
LIPOTABS™ are safe, chewable, oral liposomal tablets manufactured using patented, small molecule technology to improve bioavailability and biological effects.
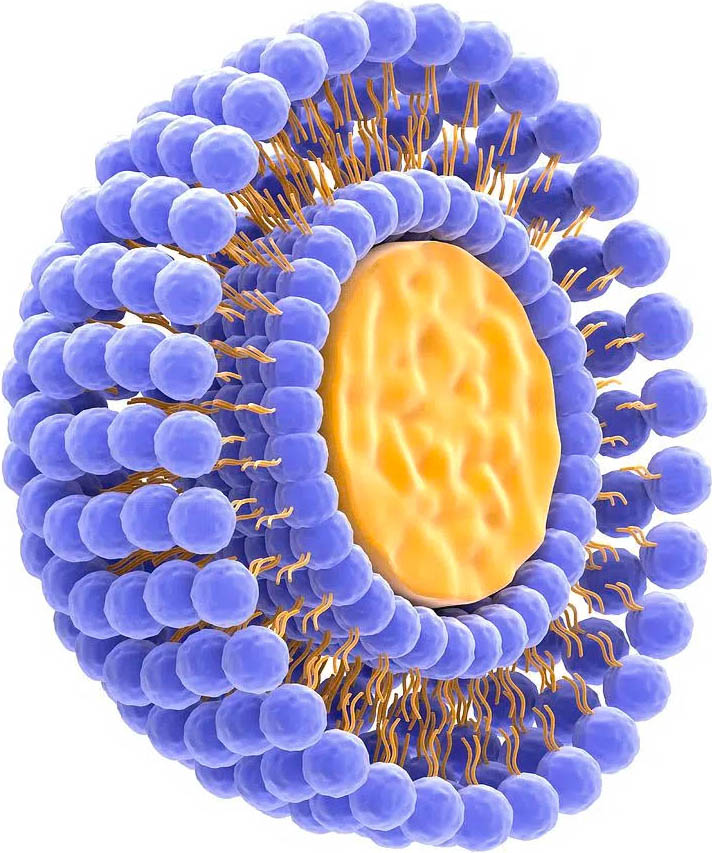
Why choose oral LIPOTABS™ (LPT™) over conventional liquid liposomes?5
- Technology invented 2018 by PHARMA scientist – patent-pending.
- LIPOTABS™ do no required heat in production.
- LIPOTABS™ are thermodynamically stable.
- No decomposition after tablet is pressed.
- No pharmacodynamic interactions.
- No substrate to facilitate reaction – unlike liquids.
- No leakage rate – actives “locked” in place w/ phospholipids.
- Stable particle size and distribution.
- The smaller the particle size, the greater bioavailability.
- LIPOTABS™ range from 60-130 nm vs. 100-300nm for liquid liposomes.
- Means lower dose for increased therapeutic effects.
- Lower potential for toxicity.
- Non-toxic excipients.*
- Tableted liposome (LIPOTAB™) much more effective dispersion than liquid liposomes.
- LPT™ particles don’t “clump” like liquid liposomes.
- Greater Bioavailability.
- Greater Stability.
- Superior Product.
- Superior Results.
LIPOTABS™ offer
several advantages also6:
- Oral drug/nutrient/peptide delivery without the need for water
- Ease of swallowing
- Some of the agent will be absorbed buccally, bypassing hepatic circulation and metabolism
- Further improved bioavailability
Electron Microscopy of the LIPOTAB™ Particles
1. Guimaraes D, et al. Design of liposomes as drug delivery system for therapeutic applications. Int J Pharm. 2021;601:12057.
2. Rajabi M, Mousa SA. Lipid nanoparticles and their application in nanomedicine. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2016;17(8):662-72.
3. Farjadian F, et al. Nanopharmaceuticals and nanomedicines currently on the market: challenges and opportunities. Nanomedicine (Lond.). 2019;14(1):93-126.
4. Lombardo D, Kiselev MA. Methods of Liposomes Preparation: Formation and Control Factors of Versatile Nanocarriers for Biomedical and Nanomedicine Application. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(3):543.
5. Ingvarsson PT, et al. Stabilization of liposomes during drying. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2011;8(3):375-88.
6. Nyamweya NN, Kimani SN. Chewable tablets: a review of formulation considerations. Pharm Technol. 2020;44(11):38-44.